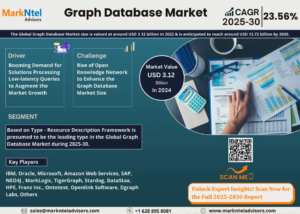
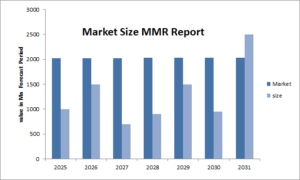
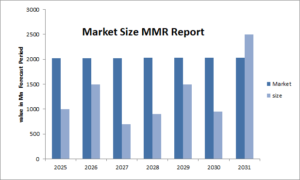
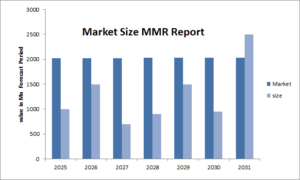
The United States Constitution serves as the bedrock of American democracy, outlining the fundamental rights and principles upon which the nation was built. Among its many provisions, the 14th Amendment has become a focal point of discussion and debate in contemporary political discourse. A recent statement made by a Biden adviser regarding the potential use of the 14th Amendment has sparked interest and raised questions about its significance in today’s political landscape.
In recent years, issues surrounding voting rights have taken center stage, with concerns about access, equality, and fairness dominating public discourse. The 14th Amendment, ratified in 1868, emerges as a potential tool to address some of these concerns. This amendment, forged in the aftermath of the Civil War, was designed to ensure equal protection under the law for all citizens, regardless of race or ethnicity. While the amendment has been pivotal in shaping the legal landscape of the United States, its contemporary application in the realm of voting rights has captured attention and drawn both support and criticism.
In this blog post, we will delve into the historical context and explore the potential implications of invoking the 14th Amendment to challenge state laws related to voting rights. By examining the historical precedents, legal interpretations, and underlying principles, we can gain a better understanding of the complexities and implications surrounding this proposal. It is crucial to consider the balance between federal and state powers, the evolving interpretation of the 14th Amendment, and the potential political ramifications that may arise from such a course of action.
Understanding the 14th Amendment
The 14th Amendment, ratified in 1868, emerged from the tumultuous aftermath of the Civil War, aiming to secure equal rights and protection under the law for all citizens. It consists of several key clauses, each addressing different aspects of citizenship, due process, and equal protection. The most relevant section to the current discussion is the Equal Protection Clause, which states that no state shall deny any person within its jurisdiction equal protection of the laws.
The Controversial Potential Application
The recent mention of the 14th Amendment by a Biden adviser has garnered attention due to its potential application in a specific context. The adviser suggested that the 14th Amendment could be invoked to challenge restrictive state laws related to voting rights. This proposition raises questions about the extent of the federal government’s authority to intervene in state legislation and the potential consequences of such a move.
Historical Precedents and Interpretations
Over the years, the 14th Amendment has been subject to different interpretations by the courts. One significant case that influenced the interpretation of the Equal Protection Clause was Brown v. Board of Education (1954), where the Supreme Court declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional. This landmark decision established the principle that the Equal Protection Clause applied not only to the federal government but also to state and local governments.
Since then, the Supreme Court has addressed various issues related to equal protection, including gender, race, and sexual orientation. These rulings have further expanded the scope of the 14th Amendment’s protections. However, the precise boundaries of its application are still subject to interpretation and ongoing legal battles.
Implications and Considerations
The potential use of the 14th Amendment to challenge state laws raises several important considerations. One key aspect is the balance between federal and state powers. The amendment empowers the federal government to intervene when states infringe upon individual rights, but it also respects the principles of federalism and the authority of states to govern their own affairs. Determining the threshold at which federal intervention is warranted remains a complex and contentious matter.
Additionally, invoking the 14th Amendment in the context of voting rights introduces a political dimension. The amendment was designed to protect individuals from discrimination, but its application to voting laws could trigger debates about the appropriate level of government involvement and the potential for partisan manipulation.
Conclusion
The 14th Amendment represents a cornerstone of constitutional law, ensuring equal protection under the law for all citizens. The recent mention of its potential application in challenging state voting laws reflects the ongoing struggle to uphold democratic principles and protect individual rights. While the precise implications and outcomes of invoking the 14th Amendment are uncertain, the ongoing discussions surrounding its use emphasize the importance of understanding and interpreting the Constitution in the context of evolving societal and political challenges. As debates continue, it is crucial for policymakers, legal scholars, and citizens to engage in thoughtful discourse and uphold the core values enshrined in the 14th Amendment while respecting the complexities of our federal system.